Architecture
Introduction
System architecture is a conceptual model that defines the structure and flow of a system. The representation of a system is contained in the mapping architecture of the relationship between one component and the other components and the principles governing its design and evolution.
Model-View-Controller-Presenter (MVCP)
The O2System Framework implements the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which is already very popular in many other php frameworks. MVC is a method for separating data (Model) from view (View) and how to process it (Controller). Then what is a Presenter, Presenter is a method to separate the logical-view from view (View). Within the O2System Framework the MVC architecture has now been evolvedinto an MVCP architecture.
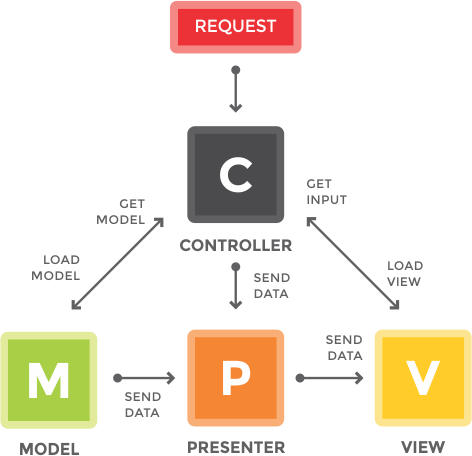
In the O2System Framework the presenter is created as a Storage Item design pattern class and is only available when the application is accessed using a browser or in other words is only active in HTTP Request mode. The presenter functions as a data processing application obtained from user-input, web-service or database. Then processed its logical view on Presenter to display in view (View).
Hierarchical Model-View-Controller-Presenter (HMVCP)
HMVCP is the evolution of the Model-View-Controller-Presenter (MVCP) architecture as described above to solve many scalability issues. In accordance with what was published on the JavaWorld website, July 2000, proposed that the three Triad, View, and Controller standards applicable in the O2System Framework be embedded in the presence of Presenters coated into "hierarchy of parent-child MCVP layers". The figure below illustrates how this works:
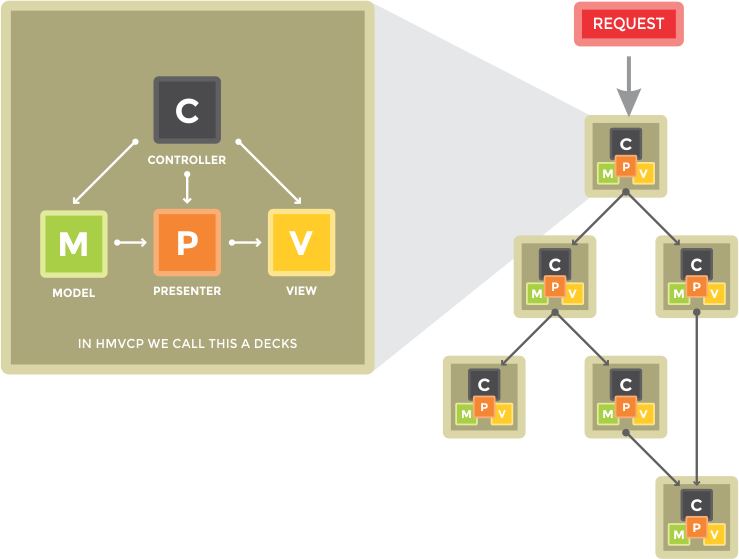
HMVCP is a collection of MVCP decks that can operate as a single mini application. Each MVCP decks are completely independent and executable in the absence of other MVCP decks. All requests made for MVCP decks must go through the controller.
The main advantages of implementing HMVCP architectures in the application development cycle are:
Modularization
Implementation of HMVCP architecture indirectly makes the application structure becomes modular.Organized
Having a directory for each of the relevant MVCP decks makes the system workload lighter.Reusable
Applying the HMVCP architecture makes the source code codes of each HMVCP decks reusable in other application projects.Easy to Maintain
Make apps easier to maintain without having to interfere with other HMVCP decks.Easy to Expand
Make apps easier to expand without sacrificing maintenance ease.
This advantage will allow you to do more exploration in your application development with less headaches.
Modular HMVCP
Modular HMVCP is an evolution of the Hierarchical Model-View-Controller-Presenter (HMVCP) architecture. HMVCP itself can be said to be a module based on its structure. But the modular architecture of HMVCP is made to perfect it.
Modular HMVCP is a package that consists of many HMVCP decks. The HMVCP Modular architecture is only available within O2System Framework and by default splits into four (4) types of modular types:
Apps
Apps are a type of package that can be called an application because it consists of a collection of packages that will be explained at the next point.Modules
Modules are a standard package type that is used as a front-office modular system. But not limited to use as back-office modular system.Components
Components are a standard package type that is used as a back-office modular system.Plugins
Plugins are standard package types that are used as add-ons functionality in the above package types.Widgets
Widgets are a standard package type that is used as an add-ons display on a modular system. Unlike the plugins widgets type does not have a controller thus making it inaccessible directly.
The greatness of the HMVCP architecture of the O2System Framework does not end here, you can create your own modular type inside with namespaces that you can set yourself.
© Copyright 2011 - 2017 with MIT License.
O2System Framework is a Trademark of Steeven Andrian Salim.